|
ARP欺骗的原理可简单的解释如下:假设有三台主机A,B,C位于同一个交换式局域网中,监听者处于主机A,而主机B,C正在通信。现在A希望能嗅探到B->C的数据,于是A就可以伪装成C对B做ARP欺骗--向B发送伪造的ARP应答包,应答包中IP地址为C的IP地址而MAC地址为A的 MAC地址。这个应答包会刷新B的ARP缓存,让B认为A就是C,说详细点,就是让B认为C的IP地址映射到的MAC地址为主机A的MAC地址。这样,B想要发送给C 的数据实际上却发送给了A,就达到了嗅探的目的。我们在嗅探到数据后,还必须将此数据转发给C,这样就可以保证B,C的通信不被中断。以上就是基于ARP 欺骗的嗅探基本原理,在这种嗅探方法中,嗅探者A实际上是插入到了B->C中,B的数据先发送给了A,然后再由A转发给C,其数据传输关系如下所示:
B----->A----->C
B<----A<------C
Windows系统中缓存了目前的MAC地址与IP地址之间的映射,通过arp -a命令可以获得,如下图:
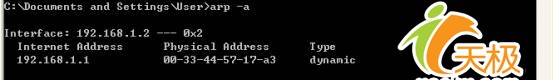
笔者的电脑IP地址为192.168.1.2,通过网关192.168.1.1到达公网。当某人用"网络剪刀手"或"网络执法官"一类的软件给笔者发送伪造的ARP报文后,笔者的Windows会缓存一个错误的网关MAC地址。由于IP包最终要通过MAC地址寻址到192.168.1.1网关进行转发,而本机对192.168.1.1 MAC地址的记录已经是错的了,这样,IP包将无法到达网关,笔者将不能再连接Internet,这就是恼人的"网络剪刀手"的工作原理。如果受到了恶意的ARP欺骗,我们只需要将网关的IP地址与MAC地址在本机静态绑定,运行如下命令:
ARP -s 192.168.1.1 00-33-44-57-17-a3
再看看此时的ARP缓存:
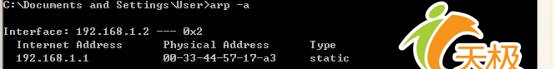
192.168.1.1一项由dynamic变成了static。
实现ARP欺骗最重要的是要组建一个ARP报文并发送给要欺骗的目标主机,下面的源代码演示了这个过程:
#define EPT_IP 0x0800/* type: IP*/
#define EPT_ARP 0x0806/* type: ARP */
#define EPT_RARP 0x8035/* type: RARP */
#define ARP_HARDWARE 0x0001/* Dummy type for 802.3 frames */
#define ARP_REQUEST 0x0001/* ARP request */
#define ARP_REPLY 0x0002/* ARP reply */
#define Max_Num_Adapter 10
#pragma pack(push, 1)
typedef struct ehhdr
{
unsigned chareh_dst[6]; /* destination ethernet addrress */
unsigned chareh_src[6]; /* source ethernet addresss */
unsigned shorteh_type; /* ethernet pachet type*/
} EHHDR, *PEHHDR;
typedef struct arphdr
{
unsigned shortarp_hrd; /* format of hardware address */
unsigned shortarp_pro; /* format of protocol address */
unsigned chararp_hln; /* length of hardware address */
unsigned chararp_pln; /* length of protocol address */
unsigned shortarp_op; /* ARP/RARP operation */
unsigned chararp_sha[6]; /* sender hardware address */
unsigned longarp_spa; /* sender protocol address */
unsigned chararp_tha[6]; /* target hardware address */
unsigned longarp_tpa; /* target protocol address */
} ARPHDR, *PARPHDR;
共4页: 上一页 1 [2] [3] [4] 下一页
|
